
In today's digital age, having a website is essential for individuals and businesses alike. It serves as your online identity and a platform to showcase your content, products, or services. WordPress, a popular content management system, makes creating a website easier than ever. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of building your own website using WordPress.

A domain name is like the digital address of your website. It's the name that people will type into their web browsers to access your site. Choosing the right domain name is crucial because it not only represents your online identity but also impacts how easily people can find and remember your website. Here are some essential considerations when selecting a domain name:
Your domain name should reflect the content, purpose, or brand of your website. For example, if you're creating a blog about healthy recipes, a domain like "HealthyEats.com" would be clear and relevant.
Short and straightforward domain names are easier to type and remember. Avoid using complicated or lengthy words that might confuse visitors.
Hyphens and numbers can be confusing and hard to remember. It's best to use letters only in your domain name.
Domain extensions are the suffixes at the end of a domain name, like .com, .org, or .net. While .com is the most popular and widely recognized, there are many other options. Consider which extension best suits your website's purpose. For instance, .org is often used by non-profit organizations, while .store is ideal for e-commerce websites.
Before you get too attached to a domain name idea, make sure it's available for registration. You can use domain registrars like GoDaddy, Namecheap, or Google Domains to check the availability of your chosen domain name.
Ensure that your domain name doesn't infringe on someone else's trademark or copyright. It's essential to choose a unique name to avoid legal troubles in the future.
Your domain name is a long-term commitment. It will become the identity of your website, so think about how it will look and sound over the years.
Consider whether your domain name has branding potential. Is it memorable? Does it have the potential to become a recognizable brand on its own?
If possible, include relevant keywords in your domain name. Keywords can help with search engine optimization (SEO) and make your website more discoverable in search results.
Once you've thought through these considerations and found a domain name that meets your criteria, you can proceed to register it through a domain registrar. Keep in mind that domain names are unique, so if your first choice is unavailable, be prepared with a list of alternatives.
Choosing the right domain name is the first step in building your online presence, so take your time and make a thoughtful decision. Your domain name is the digital front door to your website, and it plays a significant role in attracting visitors and establishing your online brand.

A hosting provider is like the home for your website on the internet. It's a service that stores all the files, data, and content of your website and makes it accessible to anyone who wants to visit your site. Choosing the right hosting provider is crucial for the performance, security, and accessibility of your website. Here's what you need to know about this step:
There are several types of hosting services available, but for most beginners and small to medium-sized websites, shared hosting and managed WordPress hosting are the most relevant options.
Shared Hosting: In shared hosting, your website shares server resources with other websites. It's an affordable option, making it suitable for beginners, but it may have limitations in terms of speed and performance.
Managed WordPress Hosting: This type of hosting is tailored specifically for WordPress websites. It's optimized for speed and security and often includes features like automatic updates and backups. Managed WordPress hosting is a bit more expensive but offers convenience and peace of mind.
Here are some key factors to consider when selecting a hosting provider:
You want a hosting provider that ensures your website is available to visitors 24/7. Look for providers with a track record of high uptime, typically 99% or higher.
Website speed is crucial for user experience and SEO. Choose a hosting provider with fast server hardware and optimized server configurations.
Good customer support is invaluable, especially if you're new to website hosting. Check if the hosting provider offers responsive support through various channels like chat, email, and phone.
Consider your future needs. Will your hosting plan allow you to easily scale up as your website grows? Scalability is important for accommodating increased traffic and content.
Website security is paramount. Look for hosting providers that offer security features like firewalls, malware scanning, and SSL certificates to keep your website safe.
Regular backups of your website are essential. Ensure that the hosting provider offers backup solutions and easy restoration in case of data loss.
Compare hosting plans and pricing to find one that fits your budget. Keep in mind that while shared hosting is cheaper, managed WordPress hosting may provide better value due to its specialized features.
A user-friendly control panel, like cPanel or a custom dashboard, makes it easier to manage your website, databases, and email accounts.
There are many hosting providers to choose from. Here are a few popular options to consider:
Bluehost: Known for its beginner-friendly approach and one-click WordPress installation.
SiteGround: Offers excellent customer support and performance optimization for WordPress.
HostGator: Provides a range of hosting options and competitive pricing.
DreamHost: Known for its commitment to open source and strong WordPress support.
Ultimately, the hosting provider you choose should align with your website's needs, budget, and growth plans. Take your time to research and read reviews to find the provider that best suits you. Once you've selected a hosting provider, you can move on to the next steps of setting up your WordPress website and making it uniquely yours.

Once you've chosen a domain name and selected a hosting provider, the next crucial step is to install WordPress on your hosting server. WordPress is a content management system (CMS) that simplifies website creation and management. Here's how to do it:
Log in to your hosting account's control panel. This is usually done through a web interface provided by your hosting provider. Popular hosting providers like Bluehost, SiteGround, and HostGator often have user-friendly dashboards.
In your hosting account's dashboard, look for an option like "One-Click Install" or "Auto Installer." This feature simplifies the process of installing WordPress by automating most of the steps.
Click on the WordPress icon or select WordPress from the list of available applications. This action will start the installation process.
You will be prompted to configure your WordPress installation:
Choose Your Domain: If you have multiple domains associated with your hosting account, select the domain where you want to install WordPress.
Directory (Optional): If you want WordPress to be installed in a specific directory (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com/blog), specify it here. If you want WordPress to be the main content of your site, leave this field blank.
Admin Credentials: Set up a username and password for your WordPress admin account. These credentials will be used to log in to your WordPress dashboard, so make them strong and secure.
Website Title and Description: Enter a title and description for your website. You can change these later in your WordPress settings.
Once you've configured the settings, click the "Install" button. The one-click installer will handle the installation process, which includes creating the necessary database and files for your WordPress website.
After a successful installation, you'll receive a confirmation message. It will usually include a link to your WordPress dashboard. Click on this link to access your new WordPress site.
You will be prompted to log in to your WordPress dashboard using the admin credentials you set up earlier. Once logged in, you can start customizing your website. You can choose a theme, add plugins, create pages and posts, and configure settings to make your website look and function the way you want.
Consider configuring essential settings in your WordPress dashboard, such as permalink structure, time zone, and reading settings. This step helps optimize your website for search engines and user experience.
That's it! You've successfully installed WordPress on your hosting server, and now you have a solid foundation to start building and designing your website. WordPress provides a user-friendly interface that allows you to create, edit, and manage content without the need for coding expertise. Enjoy the process of bringing your website to life!
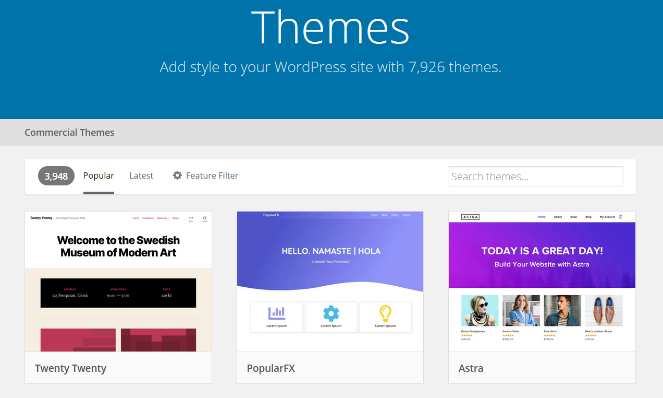
A theme is like the design template for your WordPress website. It determines how your website looks, its layout, colors, fonts, and overall style. Choosing the right theme is important because it sets the visual tone for your site and affects the user experience. Here's how to choose and apply a theme:
Log In to Your WordPress Dashboard: To get started, log in to your WordPress admin dashboard. You can usually access it by going to "yourwebsite.com/wp-admin" and entering your admin credentials.
Navigate to the "Themes" Section: In the dashboard, find the "Appearance" tab on the left-hand menu and click on it. Then, select "Themes." This will take you to the WordPress Theme Directory.
Browse Free Themes: WordPress offers a vast library of free themes. You can explore them by clicking the "Add New" button at the top of the page. Here, you can search for themes by keyword, see featured themes, or browse themes by popularity, latest additions, or specific categories.
Preview Themes: Before installing a theme, you can preview how it will look on your website. Click on a theme to see a live preview. This helps you visualize how your site might appear with that theme.
Read Theme Details: Each theme has a "Details & Preview" button. Clicking on it provides more information about the theme, including its features, customization options, and user reviews.
Install a Theme: When you find a theme you like, click the "Install" button. WordPress will download and install the theme for you.
Activate the Theme: After installation, you'll see an "Activate" button. Click it to make the theme your website's new design.
Access the Customizer: Once the theme is activated, you can start customizing it. Go back to the "Appearance" tab in the dashboard and select "Customize." Here, you can make changes to your site's appearance, such as colors, fonts, header and footer settings, and more, depending on the theme's customization options.
Theme Settings: Some themes come with their own settings panel or dashboard. Explore these settings to fine-tune your website's design and functionality further.
Consider Premium Themes: If you're looking for more advanced features, premium themes are available for purchase from third-party theme providers. These themes often offer more extensive customization options, better support, and unique designs.
Responsive Design: Ensure the theme you choose is responsive, meaning it adapts well to different screen sizes, including mobile devices.
User-Friendly: Opt for a theme that's user-friendly and easy to navigate. Simplicity often leads to better user experiences.
Compatibility: Verify that the theme is compatible with the latest version of WordPress and popular plugins.
SEO-Friendly: Choose a theme that is optimized for search engines, as this can help improve your website's visibility in search results.
Remember that you can change your theme at any time, so don't worry too much about making a permanent choice. Experiment with different themes until you find the one that best represents your website's style and functionality. The theme you choose should align with your website's purpose and appeal to your target audience.

Once you've installed and activated a WordPress theme, the next step in building your website is to customize the settings. Customizing settings allows you to tailor your website to your specific needs and preferences. Here's how to go about it:
Log In to Your WordPress Dashboard: To get started, log in to your WordPress admin dashboard using your admin credentials.
Navigate to the "Settings" Section: In the dashboard menu, you'll find a section called "Settings." Click on it to access various settings options.
General Settings: Under the "General" settings, you can configure the following:
Site Title and Tagline: Enter your website's title and a brief tagline or description. These appear on your site and in search engine results.
WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL): Ensure these are correctly set to your domain name.
Timezone: Set your website's timezone. This affects timestamps on your posts and comments.
Date and Time Format: Choose how you want dates and times to be displayed on your site.
Writing Settings: In the "Writing" settings, you can specify:
Default Post Category: Assign a default category for your posts.
Default Post Format: Choose a default format for your posts.
Post via Email: Configure settings for publishing posts via email, if desired.
Reading Settings: The "Reading" settings control how your website's front page displays:
Front Page Displays: Choose between displaying your latest posts or a static page as your homepage.
Blog Pages Show at Most: Set the number of blog posts to display on each page of your blog.
Discussion Settings: These settings relate to comments on your site:
Default Article Settings: Configure settings for new articles, including allowing or disallowing comments.
Other Comment Settings: Specify how comments are handled, including comment moderation and avatar display.
Permalink Settings: Permalinks are the URLs of your website's pages and posts. It's important to set these for SEO and user-friendliness. You can choose from various permalink structures, but the "Post Name" option is commonly recommended.
Save Changes: After making adjustments in each settings section, be sure to click the "Save Changes" button at the bottom of the page to apply your configurations.
Depending on your chosen WordPress theme, there may be additional customization options available. These settings can include:
Header and Footer Customization: Adjusting the header and footer appearance and content.
Color and Typography Customization: Changing the color scheme and font styles to match your branding.
Widget Configuration: Managing widgets in sidebars, footers, or other widgetized areas.
Menu Setup: Creating custom menus and navigation structures.
Homepage Layout: Customizing how content is displayed on your homepage.
Some themes provide their own customization options within the WordPress Customizer. To access these:
Navigate to the Customizer: In your WordPress dashboard, click on "Appearance" and then select "Customize."
Explore Theme Options: Inside the Customizer, you can explore theme-specific customization options, which may include changing the header image, site identity, or layout settings.
Customizing your website's settings allows you to tailor it to your specific needs and preferences, ensuring that it aligns with your branding and functions effectively. Take your time to explore these settings and make adjustments as needed to create the website you envision.

Essential pages are the foundation of your website, providing valuable information and facilitating user interaction. These pages serve different purposes and are crucial for engaging your audience. Here's how to create the essential pages for your WordPress website:
Log In to Your WordPress Dashboard: Start by logging in to your WordPress admin dashboard using your admin credentials.
Navigate to the "Pages" Section: In the dashboard menu, you'll find a section called "Pages." Click on it to access page management.
Add New Page: To create a new page, click the "Add New" button. This will open the page editor.
Home Page (Optional): The home page is often the first page visitors see. It should provide an overview of your website's purpose and content. Create a compelling headline, add a brief description, and consider adding elements like featured content, a welcome message, or a call to action.
About Page: The "About" page introduces you or your brand to your audience. Share your story, mission, and any relevant information that helps visitors connect with you. Consider adding photos and a brief bio.
Contact Page: The "Contact" page enables visitors to reach out to you. Create a form using a contact form plugin like "Contact Form 7" or "WPForms." Include your email address, physical address (if applicable), and social media links. Make it easy for visitors to get in touch.
Blog Page: If your website includes a blog, create a dedicated "Blog" page. This page will automatically display your latest blog posts. Ensure it's easily accessible from your main navigation menu.
Services or Products Page (If Applicable): If you offer services or products, create a dedicated page to showcase them. Provide detailed descriptions, images, prices, and any relevant information. Make it easy for visitors to make a purchase or inquire about your offerings.
Portfolio or Gallery Page (If Applicable): If you're an artist, photographer, or creative professional, consider creating a portfolio or gallery page to showcase your work. Use images and descriptions to highlight your projects and achievements.
Testimonials or Reviews Page (If Applicable): Customer testimonials and reviews can build trust and credibility. Create a page to display positive feedback from satisfied clients or customers.
Privacy Policy and Legal Pages: Ensure compliance with legal requirements by creating pages like "Privacy Policy," "Terms of Service," and "Disclaimer" if applicable to your website. Use legal plugins or templates to generate these pages.
Save and Publish: After creating each page, click the "Publish" button to make it live on your website. You can continue to edit and refine these pages as needed.
Navigation Menu: Once you've created your essential pages, add them to your website's navigation menu. Navigate to "Appearance" > "Menus" in your dashboard to customize your menu and arrange the pages in the desired order.
Page Customization: Depending on your theme, you may have options to customize the layout, design, and features of each page. Explore these options to enhance the appearance and functionality of your essential pages.
Creating essential pages is a critical step in building a comprehensive and user-friendly website. These pages provide valuable information to your visitors and help them navigate your site effectively. Make sure to keep these pages updated and relevant as your website evolves.
WordPress plugins are like add-on modules that enhance the functionality of your website. They allow you to add new features and capabilities without needing to write code. Installing the right plugins can help you customize your website and provide a better user experience. Here's how to go about it:
Log In to Your WordPress Dashboard: Start by logging in to your WordPress admin dashboard using your admin credentials.
Navigate to the "Plugins" Section: In the dashboard menu, you'll find a section called "Plugins." Click on it to access the plugins management area.
Add New Plugin: To add a new plugin, click the "Add New" button. This will take you to the plugin search and installation page.
Search for a Plugin: In the search bar, type keywords related to the functionality you want to add. For example, if you're looking for a plugin to improve SEO, you can search for "SEO."
Browse and Select a Plugin: Browse through the search results and select the plugin that suits your needs. Be sure to review the plugin's description, ratings, and user reviews to ensure it's reliable and well-maintained.
Install the Plugin: Click the "Install Now" button next to the chosen plugin. WordPress will download and install it for you.
Activate the Plugin: After installation, you'll see an "Activate" button. Click it to enable the plugin on your website.
Plugin Settings: Many plugins come with settings that you can configure to customize their behavior. These settings can usually be found in the "Settings" or "Plugins" section of your dashboard.
Here are some popular types of plugins that you might consider installing:
Yoast SEO: Enhances your website's SEO by providing tools to optimize content, meta tags, and more.
Wordfence Security: Protects your website from security threats, including malware and unauthorized access.
Sucuri Security: Offers a website firewall, malware scanning, and other security features.
W3 Total Cache: Improves your website's speed and performance by caching content and optimizing code.
Contact Form 7: Allows you to create and manage contact forms on your website.
WooCommerce: Transforms your website into an e-commerce store, enabling you to sell products or services.
ShareThis: Adds social media sharing buttons to your content, making it easy for visitors to share your posts.
UpdraftPlus: Automatically backs up your website and allows for easy restoration in case of data loss.
Google Analytics for WordPress by MonsterInsights: Integrates Google Analytics into your WordPress dashboard, providing insights into your website's traffic.
Plugin Updates: Keep your plugins updated to ensure they work smoothly and remain secure. WordPress will notify you when updates are available.
Plugin Deactivation and Deletion: If you no longer need a plugin, you can deactivate and delete it from the "Plugins" section of your dashboard.
Remember that while plugins can greatly extend your website's functionality, it's essential to use them judiciously. Too many plugins can slow down your site or cause conflicts. Choose plugins that are well-maintained, regularly updated, and genuinely add value to your website. Always back up your site before installing new plugins, just in case any compatibility issues arise.

Designing your website is a creative and essential step in creating an attractive and functional online presence. A well-designed website not only looks appealing but also ensures a positive user experience. Here's how to design your website effectively:
Log In to Your WordPress Dashboard: Start by logging in to your WordPress admin dashboard using your admin credentials.
Navigate to the "Appearance" Section: In the dashboard menu, you'll find a section called "Appearance." Click on it to access design-related options.
Select or Customize Your Theme: If you haven't already, choose a theme that reflects your website's style and purpose. WordPress offers a range of free and premium themes. You can install a theme from the WordPress Theme Directory or upload a premium theme if you have one.
Access the WordPress Customizer: Most themes allow you to customize their appearance using the WordPress Customizer. To do this, go to "Appearance" > "Customize."
Explore Customization Options: Inside the Customizer, you can explore various customization options specific to your theme. These may include:
Site Identity: Customize your site's title, tagline, and logo.
Colors: Adjust the color scheme of your website to match your branding.
Fonts: Change the font styles used for headings and body text.
Header: Customize the header area, including header image or logo.
Footer: Customize the footer area, including widgets and copyright information.
Menus: Create and customize navigation menus for your site.
Widgets: Add widgets to your sidebar, footer, or other widgetized areas.
Static Front Page: Choose whether your homepage displays your latest posts or a static page.
Preview Changes: As you make adjustments, you can see a live preview of how your website will look. This allows you to experiment with different design choices before making them permanent.
Save and Publish: Once you're satisfied with the changes, click the "Publish" button to make them live on your website.
Consider Page Builders: Some themes include built-in page builders or support popular page builder plugins like Elementor, Beaver Builder, or Divi. These tools enable you to create custom page layouts and designs with drag-and-drop functionality.
Here are some design best practices to keep in mind:
Mobile Responsiveness: Ensure your website design is responsive, meaning it adapts well to various screen sizes, including mobile devices.
User-Friendly Navigation: Make sure your website's navigation menu is clear and easy to use. Visitors should find it simple to navigate between pages and sections.
Visual Consistency: Maintain visual consistency by using a unified color scheme, fonts, and styles throughout your site.
High-Quality Images: Use high-quality images and graphics that enhance your content and don't slow down your website's loading speed.
Readable Text: Choose legible fonts and maintain proper text contrast to ensure that your content is easy to read.
Whitespace: Allow for sufficient whitespace between elements to reduce clutter and improve readability.
Call to Action (CTA): Include clear and compelling calls to action to guide visitors toward desired actions, such as signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase.
Accessibility: Ensure that your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Use alt text for images and follow web accessibility guidelines.
Browser Compatibility: Test your website's design in various web browsers to ensure it looks and functions consistently.
Remember that your website's design should align with your brand, target audience, and content. Keep it visually appealing, user-friendly, and in line with your website's goals and purpose. Regularly review and update your design to stay current with design trends and technology advancements.

Compelling content is the heart and soul of your website. It's what engages your audience, provides value, and keeps visitors coming back for more. Here's how to create content that resonates with your audience and effectively communicates your message:
Identify Your Target Audience: Before you start creating content, know who you're writing for. Understand your target audience's needs, preferences, and pain points. Tailor your content to address their interests and concerns.
Create a Content Strategy: Develop a content strategy that outlines your goals, content topics, posting schedule, and key messaging. This strategy will serve as your roadmap for creating and publishing content.
Keyword Research: If your website aims to attract organic traffic from search engines, conduct keyword research to discover relevant keywords and phrases that your audience is searching for. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner or SEMrush for this purpose.
Choose Content Types: Decide what types of content are suitable for your website and audience. Common content types include blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, podcasts, and more.
Focus on Quality: High-quality content is essential. It should be well-researched, accurate, informative, and engaging. Avoid spelling and grammar errors.
Visual Content: Incorporate visual elements like images, videos, and infographics to make your content more appealing and easier to understand.
Write Compelling Headlines: Your headlines should grab the reader's attention and clearly convey the content's purpose. Use descriptive and intriguing titles.
Engaging Introductions: Start your content with a captivating introduction that sets the stage for what follows. Make it clear why the reader should keep reading.
Structured Content: Organize your content into sections with clear headings and subheadings (H1, H2, H3, etc.). This enhances readability and helps readers find the information they seek.
Use Visuals: Include relevant images, charts, or videos to illustrate your points and break up text.
Provide Value: Your content should offer something valuable to the reader, whether it's information, entertainment, solutions to problems, or inspiration.
Be Authoritative: Back up your claims with credible sources, research, and data to build trust with your audience.
Optimize for SEO: If you want your content to be discoverable through search engines, optimize it for SEO. This includes using relevant keywords, meta descriptions, and alt tags for images.
Regular Posting: Stick to a consistent posting schedule to keep your audience engaged. Whether it's daily, weekly, or monthly, consistency matters.
Encourage Engagement: Foster interaction with your audience through comments, social media shares, and discussions. Respond to comments and messages promptly.
Regularly Review and Update: Periodically review your older content to ensure it remains accurate and relevant. Update or refresh it as needed to keep it current.
Track Analytics: Use website analytics tools like Google Analytics to monitor the performance of your content. This helps you understand what's working and what needs improvement.
Include CTAs: Encourage readers to take action, whether it's subscribing to your newsletter, making a purchase, or sharing your content. Well-placed CTAs can boost user engagement.
Remember that creating compelling content is an ongoing process. Continuously analyze your audience's feedback and adjust your content strategy accordingly. By providing valuable and engaging content, you'll build a loyal audience and establish yourself as an authority in your niche.

SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is crucial for improving the visibility of your website in search engine results. It helps attract organic (non-paid) traffic to your site. Here's how to optimize your WordPress website for search engines:
Conduct Keyword Research: Start by identifying relevant keywords and phrases related to your content. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to discover search terms that are popular among your target audience.
Long-Tail Keywords: Consider using long-tail keywords (more specific, longer phrases) to target niche topics and capture highly relevant traffic.
Optimize Content: Incorporate your chosen keywords naturally into your content, including headings, paragraphs, and meta descriptions. Ensure that your content provides valuable information related to the keywords.
Use Descriptive Headings: Organize your content with clear and descriptive headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.). This not only improves readability but also helps search engines understand the content's structure.
Optimize Images: Use descriptive file names and alt text for images to make them more accessible and SEO-friendly.
Internal Linking: Link to other relevant pages and posts within your website. This helps both users and search engines navigate your site's content.
Mobile Responsiveness: Ensure that your website is mobile-responsive. Google places significant importance on mobile-friendly websites.
Site Speed: Optimize your website's loading speed. Faster websites tend to rank higher in search results. You can use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to assess and improve site speed.
XML Sitemaps: Generate and submit an XML sitemap of your website to search engines like Google. This helps search engines index your site's pages more efficiently.
Schema Markup: Implement schema markup (structured data) to provide search engines with additional information about your content. This can enhance how your content appears in search results.
SSL Certificate: Ensure your website has an SSL certificate, which encrypts data and provides a secure browsing experience. Google considers SSL a ranking factor.
Permalink Structure: Use SEO-friendly permalink structures. In WordPress, the "Post Name" option is recommended. This makes your URLs descriptive and readable.
High-Quality Content: Continue to create high-quality, informative, and engaging content. Quality content is more likely to attract organic backlinks, which can boost your SEO.
Backlinks: Earn high-quality backlinks from reputable websites. These links act as endorsements of your content's value and can improve your search engine rankings.
Social Signals: While not a direct ranking factor, social media presence and shares can indirectly impact your SEO by increasing brand visibility and driving traffic.
User-Friendly Design: Ensure your website is easy to navigate and provides a good user experience. This includes mobile optimization, fast loading times, and clear calls to action.
Reduce Bounce Rate: Keep visitors engaged by providing valuable content and reducing bounce rates (the percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page).
Responsive Design: Optimize your website for different devices and screen sizes to improve the user experience.
Monitor SEO Performance: Regularly check your website's SEO performance using tools like Google Analytics and Google Search Console. Track your rankings, organic traffic, and user behavior.
Adjust Your Strategy: Based on your monitoring, make adjustments to your SEO strategy. This may involve refining your content, optimizing technical aspects, or building more backlinks.
SEO is an ongoing process, and it's essential to stay updated with the latest SEO trends and best practices. By consistently optimizing your website for search engines, you'll increase its visibility and attract more organic traffic over time.

Responsiveness is a critical aspect of web design, ensuring that your website looks and functions well on various devices and screen sizes. Testing responsiveness is vital to provide an excellent user experience to all your visitors, whether they're using a desktop computer, tablet, or smartphone. Here's how to test and ensure your WordPress website is responsive:
Log In to Your WordPress Dashboard: Begin by logging in to your WordPress admin dashboard using your admin credentials.
Preview on Different Devices: One of the simplest ways to test responsiveness is to use the built-in preview feature in your web browser. Open your website in a web browser (Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, etc.).
Resizing the Browser Window: While viewing your website, resize the browser window by dragging its edges. Observe how your website content adapts to different widths. Pay attention to:
Text and Font Sizes: Ensure text remains readable and properly scaled.
Images and Graphics: Check that images resize and reposition appropriately.
Navigation Menu: Verify that the navigation menu remains accessible and user-friendly on smaller screens.
Online Testing Tools: Several online tools can help you test your website's responsiveness across various devices and screen sizes. Here are a few popular ones:
Google Mobile-Friendly Test: Enter your website URL, and Google's tool will analyze your site's mobile-friendliness and provide suggestions for improvement.
BrowserStack: BrowserStack allows you to test your website on different browsers and devices. You can choose from a wide range of mobile and tablet devices for testing.
Responsinator: Responsinator provides a quick way to view how your site appears on various devices, including tablets and smartphones.
Mobile Emulators: Some web development tools and software offer mobile device emulators that simulate how your website looks and functions on specific devices and screen sizes. Popular options include:
WordPress Customizer: If your theme supports it, you may find mobile device previews within the WordPress Customizer.
Browser Developer Tools: Most web browsers offer developer tools that include mobile device emulators. You can access these by right-clicking on your web page and selecting "Inspect" or "Inspect Element." In the developer tools, look for options like "Toggle Device Toolbar" or "Responsive Design Mode."
Accessibility Testing: Alongside responsiveness, consider conducting accessibility testing to ensure that your website is usable by people with disabilities. Tools like WAVE or Axe can help identify and address accessibility issues.
Review and Adjust: As you test your website's responsiveness, take note of any issues or elements that don't display correctly on different devices. Use your WordPress theme's customization options or CSS to make adjustments as needed.
Retest: After making adjustments, be sure to retest your website's responsiveness to confirm that the issues have been resolved.
By thoroughly testing your website's responsiveness, you'll ensure that it provides an optimal user experience to all your visitors, regardless of the device they use. A responsive website can lead to higher user satisfaction and improved search engine rankings, as search engines value mobile-friendly design.
Checking for errors is a crucial part of maintaining a functional and user-friendly WordPress website. Errors can negatively impact user experience, SEO rankings, and the overall performance of your site. Here's how to identify and address common errors:
Functionality Testing: Regularly test all the features and functions of your website to ensure they work as intended. Pay attention to forms, buttons, navigation menus, and interactive elements. Make sure users can perform actions like submitting forms, adding items to the cart (if applicable), and accessing all pages.
Link Checking: Check for broken links throughout your site. Broken links can frustrate users and harm your SEO. You can use online tools or WordPress plugins to scan for broken links and fix them.
Content Accuracy: Review your content periodically to ensure accuracy. Check for outdated information, incorrect details, or missing content. Update or correct any errors you find.
SEO Auditing: Perform SEO audits using tools like Google Search Console or third-party SEO plugins to identify issues such as crawl errors, duplicate content, or missing meta tags. Address these issues to improve your website's search engine rankings.
Security Scans: Conduct regular security scans to detect vulnerabilities or malware on your website. Use WordPress security plugins and follow best practices to protect your site from threats.
Form Testing: If your website includes contact forms, subscription forms, or any other type of user input forms, test them regularly to ensure they function correctly. Verify that form submissions are being received, and the data is stored or forwarded appropriately.
Performance Testing: Monitor your website's performance by assessing its loading speed. Slow-loading pages can lead to high bounce rates and lower search engine rankings. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify performance issues and optimize your site accordingly.
Mobile Responsiveness: Reiterate the importance of mobile responsiveness. Test your website's appearance and functionality on various mobile devices to ensure a consistent and user-friendly experience.
Browser Compatibility: Verify that your website displays correctly and functions well on different web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, etc.). Cross-browser testing helps ensure a consistent experience for all users.
HTML and CSS Validation: Validate your website's HTML and CSS code to ensure it follows web standards. Errors in your code can lead to rendering issues and compatibility problems. Online validation tools can help you identify and fix code errors.
Backup Verification: Ensure that your website's backup system is working correctly. Regularly test the restoration process to confirm that you can recover your site in case of data loss or other emergencies.
Accessibility Testing: Conduct accessibility audits to ensure your website complies with accessibility standards (e.g., WCAG). Accessibility errors can prevent some users, such as those with disabilities, from accessing your content. Tools like WAVE or Axe can help identify and resolve accessibility issues.
Continuous Monitoring: Make error checking and monitoring a routine part of your website maintenance process. Set up alerts or notifications to be informed of issues as they arise.
Immediate Action: Address any errors or issues you discover promptly. This includes fixing broken links, updating content, applying security patches, and resolving technical errors.
Regularly checking for errors and conducting maintenance tasks will help keep your WordPress website running smoothly, improve user satisfaction, and ensure that your site remains secure and functional over time.

Backing up your WordPress website is a critical step in ensuring the security and integrity of your site's data. It safeguards your content, files, and configurations, allowing you to recover your site in case of data loss, security breaches, or technical issues. Here's how to properly back up your WordPress website:
Choose a Backup Method: There are several methods for backing up your WordPress site:
Manual Backups: You can manually back up your website by downloading your files and databases using FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and phpMyAdmin. This method provides full control but can be time-consuming.
Web Hosting Backups: Many web hosting providers offer automated backup solutions. Check if your hosting provider provides daily or regular backups and how to access them.
WordPress Backup Plugins: Consider using WordPress backup plugins like UpdraftPlus, BackupBuddy, or VaultPress. These plugins simplify the backup process and allow you to schedule automatic backups.
Set a Backup Schedule: Determine how often you should back up your website. Daily or weekly backups are recommended for most websites, while high-traffic or frequently updated sites may benefit from more frequent backups.
Full Backups vs. Partial Backups: Decide whether you want to create full backups (including files and databases) or partial backups (specifically, files or databases). Full backups provide comprehensive protection but may consume more storage space.
Choose a Storage Location: Store your backups in a secure location, separate from your web server. Options include:
Cloud Storage: Services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or Amazon S3 offer reliable cloud storage solutions for your backups.
Local Storage: Save backups to your local computer or an external hard drive. However, this method may not be as secure in the event of hardware failures or disasters.
Use Backup Plugins: If you opt for a backup plugin, install and configure it according to your preferences. Most backup plugins allow you to schedule automatic backups and choose storage destinations.
Verify Backup Integrity: Periodically test your backups by restoring them to a test environment to ensure they are complete and functional.
Manual Backups: If you choose to perform manual backups, use FTP to download your website files, and use phpMyAdmin to export your WordPress database. Save these files securely.
Create a Restoration Plan: In case of emergencies, outline a step-by-step plan for restoring your website from backups. Include instructions for accessing backups and reinstalling WordPress if necessary.
Retention Policy: Define a retention policy for your backups. Determine how long you will retain old backups and when you will delete them to manage storage space efficiently.
Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor your backup process to ensure backups are running as scheduled and without errors.
Offsite and Offserver Backups: Keep at least one copy of your backups offsite (external cloud storage) and off the web server to safeguard against server failures or hacking incidents.
Encryption and Security: If your backups contain sensitive data, consider encrypting them to protect against unauthorized access.
By following these steps and maintaining a reliable backup system, you can protect your WordPress website and quickly recover from unexpected issues, ensuring minimal disruption to your online presence. Remember to test your restoration process periodically to guarantee the effectiveness of your backup strategy.

Domain configuration refers to the process of setting up and managing your website's domain name, which is the web address that visitors use to access your site (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com). Proper domain configuration is essential for ensuring that your domain points to the correct web hosting server and that your website functions as expected. Here's how to manage your domain configuration effectively:
Choose a Domain Registrar: A domain registrar is a company or service where you purchase and manage your domain name. Popular registrars include GoDaddy, Namecheap, Google Domains, and many others. If you haven't already, choose a reputable registrar and create an account.
Access Domain Settings: After logging in to your domain registrar's account, navigate to the domain management section. This is where you'll configure your domain settings.
DNS (Domain Name System) Configuration: DNS settings determine how your domain name connects to your web hosting server. You'll typically find options for:
Nameservers: Set the nameservers provided by your web hosting provider. These nameservers guide visitors' browsers to the correct server where your website files are hosted.
A Records: Configure A (Address) records to map your domain to the specific IP address of your hosting server. This ensures that your domain points to the right location.
Domain Forwarding (Optional): If you have multiple domains or want to forward one domain to another (e.g., redirecting www.yourwebsite.net to www.yourwebsite.com), configure domain forwarding settings as needed.
SSL Certificate Installation: If your website uses HTTPS for secure browsing (recommended for all websites), ensure that your SSL certificate is correctly installed and configured. Most web hosts offer free SSL certificates, and you can often set them up directly from your hosting control panel.
Email Setup (Optional): If you want to use a custom domain email address (e.g., info@yourwebsite.com), configure your domain's email settings through your hosting provider or email hosting service.
MX Records (Mail Exchanger Records): If you're using a separate email hosting service, configure MX records to route incoming emails to the correct mail servers.
Subdomain Configuration (Optional): If you want to create subdomains (e.g., blog.yourwebsite.com), set up subdomain records in your DNS settings. This allows you to host different sections of your site on separate subdomains.
Domain Renewal: Ensure your domain registration remains active by monitoring its expiration date and renewing it promptly through your registrar.
Domain Privacy (Optional): Consider enabling domain privacy protection (WHOIS privacy) to keep your personal contact information hidden from public WHOIS records. This helps protect your privacy and reduce spam.
Testing: After making any changes to your domain settings, test your website to ensure it's accessible via the domain name. Also, verify that email services (if used) are functioning correctly.
Documentation: Keep records of your domain configuration settings, including nameservers, DNS records, SSL certificates, and domain renewal dates. This documentation is invaluable for troubleshooting and future reference.
Proper domain configuration is essential for a seamless online presence. By following these steps and regularly reviewing your domain settings, you can ensure that your domain name is correctly connected to your website, email services, and other online resources. This helps maintain the accessibility and functionality of your WordPress website.

Announcing your website is a crucial step to let the world know that your WordPress website is live and ready for visitors. Effective announcements can help drive initial traffic, engage your target audience, and build awareness about your online presence. Here's how to effectively announce your website:
Share on Social Media: Use your business or personal social media accounts (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn) to announce the launch of your website. Craft engaging posts that include a link to your site and a brief description of what visitors can expect.
Leverage Hashtags: Use relevant hashtags to increase the visibility of your social media posts. Research popular and industry-specific hashtags related to your website's content or niche.
Engage with Your Audience: Respond to comments, questions, and feedback from your social media followers to create a sense of community and show that you value their interactions.
Email Announcement: If you have an email newsletter or subscriber list, send out an email announcing your website's launch. Include a link to the site, a compelling subject line, and a brief message about what readers can find on your website.
Write a Launch Blog Post: Create a blog post on your website itself announcing its launch. Share the story of your website's journey, its purpose, and what visitors can expect to find. Include images and visuals to make the post engaging.
Share on Social Media: Promote your launch blog post on your social media platforms to redirect traffic back to your website.
Press Release (Optional): If your website launch is significant or related to a business or organization, consider crafting a press release. Distribute it to relevant media outlets and online news sources to generate publicity.
Share on Online Communities: If your website serves a particular niche or community, share the announcement on relevant online forums, discussion boards, or community groups where your target audience gathers.
Collaborate with Influencers: If possible, collaborate with influencers or industry experts who can promote your website to their followers. Their endorsement can help increase your website's visibility.
Paid Advertising (Optional): Consider running paid advertising campaigns on platforms like Google Ads or social media to promote your website to a broader audience.
Track Engagement: Use analytics tools to monitor the engagement and traffic generated by your announcements. This data can help you assess the effectiveness of your promotion strategies.
Collect Feedback: Encourage visitors to provide feedback on your website's content, design, and usability. Use this input to make necessary refinements and improvements.
Stay Active: After the initial announcement, continue to stay active on your website and social media platforms. Consistently publish new content, engage with your audience, and keep your website up to date.
Announcing your website's launch is an exciting moment that marks the beginning of your online journey. By strategically promoting your website through various channels, engaging with your audience, and providing valuable content, you can build a strong online presence and attract a growing number of visitors to your WordPress website.

In conclusion, launching a WordPress website involves a series of steps that require careful planning and execution. By following these steps, you can create a successful and engaging online presence. Here's a recap of the key points covered in each step:
Choose a Domain Name: Select a domain name that reflects your brand, is easy to remember, and aligns with your website's purpose.
Select a Hosting Provider: Pick a reliable web hosting provider that offers the features and resources your website needs.
Install WordPress: Install WordPress on your hosting server using the provided tools or manual installation.
Choose a Theme: Select a WordPress theme that suits your website's design and functionality requirements.
Customize Settings: Configure WordPress settings, including site title, tagline, permalinks, and reading settings.
Create Essential Pages: Create essential pages such as the homepage, about page, contact page, and any others relevant to your website.
Install Plugins: Enhance your website's functionality by installing plugins for SEO, security, performance, and other features.
Design Your Website: Customize your website's design by adjusting colors, fonts, layouts, and adding logos or graphics.
Create Compelling Content: Develop high-quality, engaging content that resonates with your target audience.
SEO Optimization: Optimize your website for search engines to improve its visibility in search results.
Test Responsiveness: Ensure your website looks and functions well on various devices and screen sizes.
Check for Errors: Regularly monitor your website for errors, broken links, and issues that could affect user experience.
Backup Your Website: Implement a robust backup system to protect your website's data and content.
Domain Configuration: Properly configure your domain settings to ensure your website is accessible through your chosen domain name.
Announce Your Website: Promote your website's launch through social media, email, blog posts, and other channels to attract visitors and build awareness.
By diligently following these steps and continually maintaining and improving your website, you can create a successful WordPress website that meets your goals, engages your audience, and establishes your online presence effectively. Remember that building and maintaining a website is an ongoing process, and staying committed to providing value to your visitors is key to long-term success.
PosTwinkle, AgencyTwinkle, MartVill, HelpDesk, Organis, GroStore, Varient, Maan, 6Valley, GainPos, SmartHospital, UltimateInventory
Visit our website: twinklerain.com